|
|

Your download link is at the very bottom of the page... always. |
Processed through Paypal No account required. |
Buy our over-priced crap to help keep things running.










|
|

Your download link is at the very bottom of the page... always. |
Processed through Paypal No account required. |










| File - Download Windows 11 Requirements Check Tool v1.4.0 | ||||||||
| Description | ||||||||
|
A plea... Deanna and I have been running this site since 2008 and lately we're seeing a big increase in users (and cost) but a decline in percentage of users who donate. Our ad-free and junkware-free download site only works if everyone chips in to offset the revenue that ads on other sites bring in. Please donate at the bottom of the page. Every little bit helps. Thank you so much. Sincerely, your Older Geeks: Randy and Deanna Always scroll to the bottom of the page for the main download link. We don't believe in fake/misleading download buttons and tricks. The link is always in the same place. Windows 11 Requirements Check Tool v1.4.0 A free tool to see if your PC meets the requirements to run Windows 11. In addition it checks if your PC can support (gaming) features like AutoHDR and DirectStorage. Runs on Windows 8.1, Windows 10 or Windows 11. Supports 32-bit and 64-bit systems, including Windows on ARM. This tool is a standalone Win32 application written in C++. It does not install anything and spawns no additional processes. Requirement Checks The tool performs the following checks as specified in this document from Microsoft: System Type Shows whether your PC contains an x86, x64 or ARM-processor. In addition it shows if your operating system is 32-bit or 64-bit. This item turns red if your processor does not support 64-bit instructions and registers, also known as long mode. Windows Shows the version of Windows you are running. This item checks if your version of Windows can be upgraded to Windows 11. Processor Shows the processor in your computer. This item checks if your processor has at least 2 cores and runs at 1 GHz or higher. In addition, this item also checks if your processor supports the following features and instructions:
Note that the tool does not use a list of supported processors but actually checks various feature bits reported by the processor. Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) Shows if your processor has hardware support for Hypervisor-Enforced Code Integrity (HVCI). HVCI protects Windows from compromise by bad drivers and malicious system files. Processors that support HVCI in hardware provide significant performance improvements. Intel's Mode-Based Execute Control for EPT (MBEC), AMD's Guest-Mode Execute Trap for NPT (GMET) and ARM's Translation Table Stage 2 Unprivileged Execute-Never (TTS2UXN) are features that provide this hardware support. The tool checks if these features are available in the processor. For more information on Virtualization-Based Security see this blog item. Note that there is discussion regarding Intel 7th generation and AMD Zen 1 processors not being supported by Windows 11. Yet these processors do have the aforementioned features to support HVCI in hardware. Read this blog post for more information. System Memory Shows the amount of physical memory installed in your PC. This item turns red if the amount is less than 4GB. Storage Shows the capacity of the system volume. This item turns red if the capacity is less than 64GB. BIOS Mode Shows if the PC uses UEFI or legacy firmware. This item turns red if the PC uses legacy firmware to boot the computer. Secure Boot Shows if the PC uses Secure Boot. This item turns green if Secure Boot is enabled. This item turns orange if your computer is capable to support Secure Boot. This item turns red if your system disk is formatted as MBR and therefore incapable to use Secure Boot. Security Processor Shows if the PC has a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) enabled. In addition, it checks whether the TPM supports TPM 2.0. Turns orange if your TPM only supports version 1.2. A TPM chip is a secure crypto-processor that helps with actions such as generating, storing, and limiting the use of cryptographic keys. It adds hardware-based security benefits to Windows in the following business-focused features:
Display Verifies whether the size of your display is at least 9 and supports a resolution of 720p or higher. The tool queries the Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) from the display to determine this information. Graphics Verifies whether your display adapter (graphics card) supports DirectX 12 and WDDM 2.0. Note that this information is gathered from the currently installed drivers. Feature Checks The tool performs the following Windows 11 feature checks. Each of these checks are shown orange if your system does not support the feature. This as these features are not required in order to run Windows 11. See this page for more information on feature requirements. AutoHDR This item checks if any of your currently connected displays support High Dynamic Range (HDR) content. Windows 11 introduces AutoHDR which adds HDR to games that do not support HDR, therefore improving graphics quality and immersive feeling. DirectStorage This item checks the Storage Controller of your system disk and the Shader Model of your graphics card (GPU) to see if they meet DirectStorage requirements. DirectStorage is a feature that allows games to load quickly by working to load assets on the GPU, saving resources on the CPU and as such helps to improve graphics and reduce load times. If you have a hybrid system (eg. gaming laptop) containing both an integrated and discrete GPU, the tool will use the discrete GPU for the validation. Note that Microsoft recently announced that it will bring DirectStorage to Windows 10 as well. Changes 1.4.0 - 2022-01-31 Several improvements to the user interface Added support for additional Intel Alder Lake processors SHA-256: D9D5B69E67BDB7ED99D25387ED4F593E11BE2261B480CE75A5EB36C62CE9C4CF 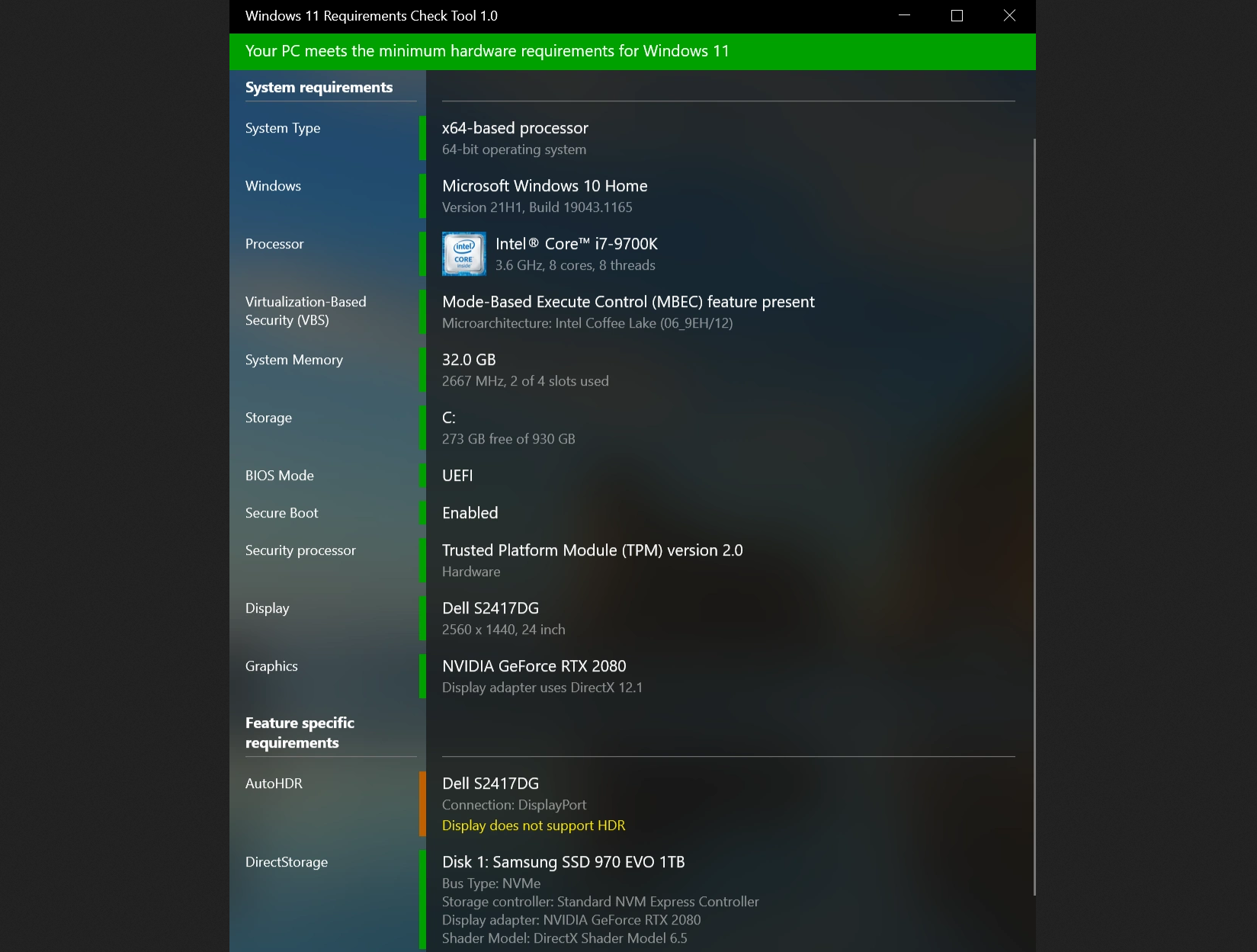 Click here to visit the author's website. Continue below for the main download link. |
||||||||
| Downloads | Views | Developer | Last Update | Version | Size | Type | Rank | |
| 2,363 | 7,794 | ByteJams.com <img src="https://www.oldergeeks.com/downloads/gallery/thumbs/Win11ReqCheck1_th.png"border="0"> | Feb 01, 2022 - 11:30 | 1.4.0 | 447.9KB | ZIP |  , out of 50 Votes. , out of 50 Votes. |
|
| File Tags | ||||||||
| Windows 11 Requirements Check Tool v1.4.0 | ||||||||
|
Click to Rate File Share it on Twitter → Tweet
|